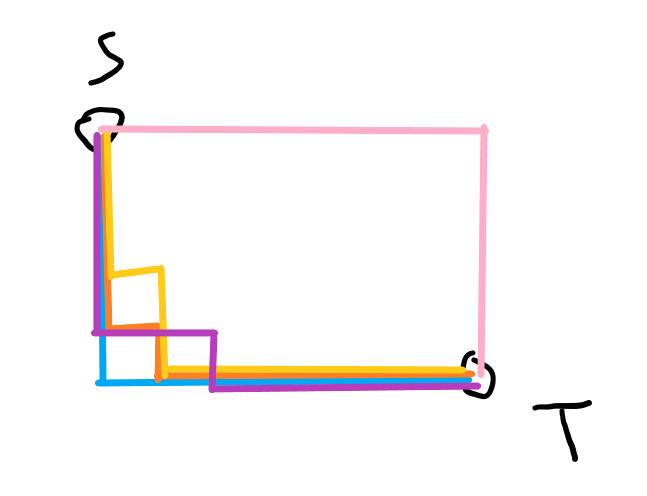紫名后第一次没跑路的场,好像黄了
熬夜等分,成功了,感觉还是挺快乐的
1358A Park Lighting 一个点最多照两个,而且一定能组合,除非总数是奇数,会多用一个。
a.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;int main () int q; cin >> q; while (q--) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; a *= b; if (a & 1 ) cout << a / 2 + 1 << endl ; else cout << a / 2 << endl ; } return 0 ; }
1358B Maria Breaks the Self-isolation 按要求的从小到大排序,每次检测当前的大妈要求是否可行,一次打电话全叫来。
b.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;typedef vector <int > vi;int main () int q; cin >> q; while (q--) { int n; cin >> n; vi a (n) ; for (int &i : a) cin >> i; sort(a.begin (), a.end ()); int ans = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { if (i + 1 >= a[i]) ans = i + 2 ; } cout << ans << endl ; } return 0 ; }
1358C Celex Update 首先可以想到,最大值是蓝色路径,最小值是粉色路径。那么比最大值小 $1$ 的就是橙色路径,再小 $1$ 的就是黄色和紫色路径了,那么可以想到只有 $(x_2-x_1)\times (y_2-y_1)+1$中取值。
c.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;typedef long long ll;int main () int q; cin >> q; while (q--) { ll x1, y1, x2, y2; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2; y2 -= y1; x2 -= x1; cout << x2 * y2 + 1 << endl ; } return 0 ; }
1358D The Best Vacation 可以想到 $x=1$ 时一定是要取最大的$d_i$,$x=2$ 时再取 $d_i-1$,依次类推,那么答案的有边界一定会在某个月的最后一天了。
d.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;typedef long long ll;int main () auto calc = [](ll x) { return (1 + x) * x / 2 ; }; int n; ll x; cin >> n >> x; vector <int > d (n * 2 + 1 ) for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { cin >> d[i]; d[i + n] = d[i]; } n *= 2 ; ll tx = 0 , ans = 0 , a = 0 , b = 1 , tmp = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { tx += d[i]; tmp += calc(d[i]); while (tx > x) { ll t = min (tx - x, d[b] - a); tx -= t; tmp -= calc(t + a) - calc(a); a += t; if (a == d[b]) { ++b; a = 0 ; } } ans = max (ans, tmp); } cout << ans << endl ; return 0 ; }
1358E Are You Fired? 首先按分类讨论下:
$x>0$,如果 $n$ 个数求和是整数,那么直接汇报,此时 $k=n$。
否则,$k >= \lceil \frac {n}{2} \rceil + 1$,首先想到枚举最右的 $i(n-k+1$,也就是枚举 $k$),然后我们从右向左判断后缀和 $suf[i] - suf[i+k] > 0$ 是否均成立,这一步由于回溯是 $n^2$ 的;
然而又可以想到,如果对于 $j$ 有 $suf[i] - suf[i+k] < 0$ 不成立,那么对于更大的 $k$,都会是使式不成立,因此下一次枚举直接从 $j-1$ 继续即可,那么每个位置只会访问一遍,不需要回溯,$O(n)$。
e.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 using namespace std; typedef long long ll; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<ll> a(n + 5), sum(n + 5); ll x, t = 0; int m = (n + 1) / 2; for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { cin >> a[i]; t += a[i]; } cin >> x; if (x > 0) { if (t + x * (n / 2) > 0) { cout << n << endl; return 0; } else { cout << -1 << endl; return 0; } } for (int i = n; i >= 0; --i) { if (i > m) a[i] = x; sum[i] = sum[i + 1] + a[i]; } int ans = -1; for (int i = m, j; i >= 0; --i) { if (sum[i] > 0) { int f = 1; for (j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { if (sum[j] - sum[j + n - i + 1] <= 0) { f = 0; break; } } if (f == 1) { ans = n - i + 1; break;; } i = j; } } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
本文标题: Codeforces Round 645 Div.2 题解
文章作者: WGree
发布时间: 2020-05-27
最后更新: 2020-05-27
原始链接: https://blog.wgree.site/613236291/
版权声明: 禁止转载